Are you looking to shed some extra pounds and wondering if low-energy-density foods hold the key to successful weight loss?
In this comprehensive article, we’ll delve into the intriguing relationship between low-energy-density foods, satiety, and effective weight management. You’ll discover how incorporating low-energy-density foods into your diet can help you feel full and satisfied while consuming fewer calories.
But that’s not all – we’ll also explore essential factors that play a pivotal role in your quest for a healthier, more balanced lifestyle, ensuring you’re well-equipped with the knowledge needed to embark on a successful weight loss journey.
So, if you’re ready to uncover the secrets of achieving satiety, managing your weight, and making informed dietary choices, let’s dive right in.
- What Are Low Energy Density Foods?
- Which Foods Have the Lowest Energy Density?
- Low Energy Dense Recipes
- High Energy Density Foods
- How Much Do Low Energy Dense Foods Impact Satiety?
- But Is Low-Fat Really Where It’s At?
- Do High-Volume Foods Make You Feel Fuller for Longer?
- Satiety vs Satiation
- What Other Factors Align With Satiety?
- Does Adding Water to Your Meal Help?
- Multivariate Analysis
- Diet Quality Is King!
- How Can I Reduce My Energy Intake?
- Nutrient-Dense Foods
- Nutrient-Dense Recipes
- More
What Are Low Energy Density Foods?
To put it simply, low-energy density foods contain fewer calories per gram (weight) of food.
Energy density = calories ÷ weight
The energy density of food is generally shown as calories per gram of food.
If it isn’t listed on the label, the weight of the food can be calculated by summing:
- water,
- protein,
- fibre,
- carbohydrates,
- fat, and
- ash.
Weight, on the other hand, is always shown on labels and in food databases. So, for the purpose of this article, we will look at calories per unit of weight.
Which Foods Have the Lowest Energy Density?
Is apple low energy density? What about potatoes, chard or grapes?
To give you an idea of what low-energy foods look like in practice, we have provided a list of low-energy density foods below, sorted from lowest to highest energy density.
Plant-Based Foods – Low Energy Density Foods List
It’s probably not surprising that plant-based foods have the lowest energy density, particularly non-starchy vegetables.
| food | calories/100 g |
| watercress | 11 |
| kimchi | 15 |
| cucumber | 15 |
| endive | 17 |
| zucchini | 17 |
| lettuce | 17 |
| Swiss chard | 19 |
| coconut water | 19 |
| sauerkraut | 19 |
| green peppers | 20 |
| asparagus | 20 |
| alfalfa sprouts | 23 |
| cabbage | 23 |
| cauliflower | 25 |
| broccoli | 26 |
| watermelon | 30 |
| chives | 30 |
| cantaloupe | 34 |
| parsley | 36 |
| onion | 40 |
| pears | 42 |
| butternut squash | 45 |
| oranges | 47 |
| kale | 49 |
| raspberries | 52 |
| apples | 52 |
| leeks | 61 |
| kiwifruit | 61 |
| cherries | 63 |
| grapes | 67 |
| green peas | 81 |
| sweet potato | 90 |
These foods will be challenging to overeat, especially if you don’t add extra fat or dressings.
Animal and Seafood – Low Energy Density Foods List
There are some lower energy-density seafood and animal-based foods.
| food | calories/100 g |
| milk (low fat) | 42 |
| oysters | 51 |
| egg white | 52 |
| Greek yogurt (low fat) | 59 |
| cottage cheese (low fat) | 74 |
| crayfish | 82 |
| crab | 83 |
| haddock | 90 |
| halibut | 91 |
| squid | 92 |
| tilapia | 96 |
| Greek yogurt | 97 |
| Canadian bacon | 110 |
| beef heart | 112 |
| shrimp | 119 |
| beef liver | 135 |
| lamb liver | 139 |
| whole egg | 143 |
| ground chicken | 143 |
However, these foods typically contain more fat and less water than plant-based foods, giving them a higher energy density.
Note: Fat provides nine calories per gram, whereas carbohydrates provide around four calories per gram.
Low Energy Dense Recipes
To give you a feel for what recipes with fewer calories per gram look like, we have some example low-energy density NutriBooster Recipes below:
- green nutrient-boosting smoothie
- low-calorie panna cotta
- Sue’s salad
- cauliflower & spinach soup (pictured)
- roast turmeric cauliflower
- sautéed radish & watercress
You will note that these tend to be smoothies, soups, and salads.
High Energy Density Foods
For comparison, we’ve listed some examples of popular energy-dense foods. These may be ideal if you are lean, very active and thus need more energy. However, they are likely not optimal if your goal is to eat fewer calories and lose body fat.
Plant-Based – High Energy Density Foods List
Nuts and plant-based oils have the highest energy density. These energy-dense foods would be much easier to overconsume.
| food | calories/100 g |
| coconut oil | 900 |
| olive oil | 900 |
| pecans | 691 |
| Brazil nuts | 659 |
| walnuts | 654 |
| nut butter | 590 |
| cashews | 580 |
| almonds | 579 |
| sesame seeds | 573 |
| pistachio nuts | 560 |
| flaxseeds | 534 |
| peanuts | 599 |
| prunes | 339 |
| turmeric | 312 |
| whole wheat bread | 278 |
| rye bread | 259 |
| oat bran | 246 |
| coconut milk | 230 |
Animal-Based Foods – High Energy Dense Foods List
High-fat animal-based foods tend to have a high energy density, so the weight of food to reach your daily calorie budget would be fairly low.
| food | calories/100 g |
| butter | 718 |
| pepperoni | 504 |
| Parmesan cheese | 420 |
| bacon | 417 |
| Gruyere cheese | 413 |
| Swiss cheese | 393 |
| salami | 368 |
| Edam cheese | 357 |
| blue cheese | 353 |
| provolone cheese | 351 |
| cream cheese | 350 |
| brie | 334 |
| Braunschweig | 327 |
| liverwurst | 326 |
| egg yolk | 322 |
| liver pate | 319 |
Some people report that they feel full quickly on these foods, but this may be because they have been able to consume a lot of calories quickly. Unfortunately, without precisely tracking your food, it’s hard to judge satiety per calorie just by how you feel.
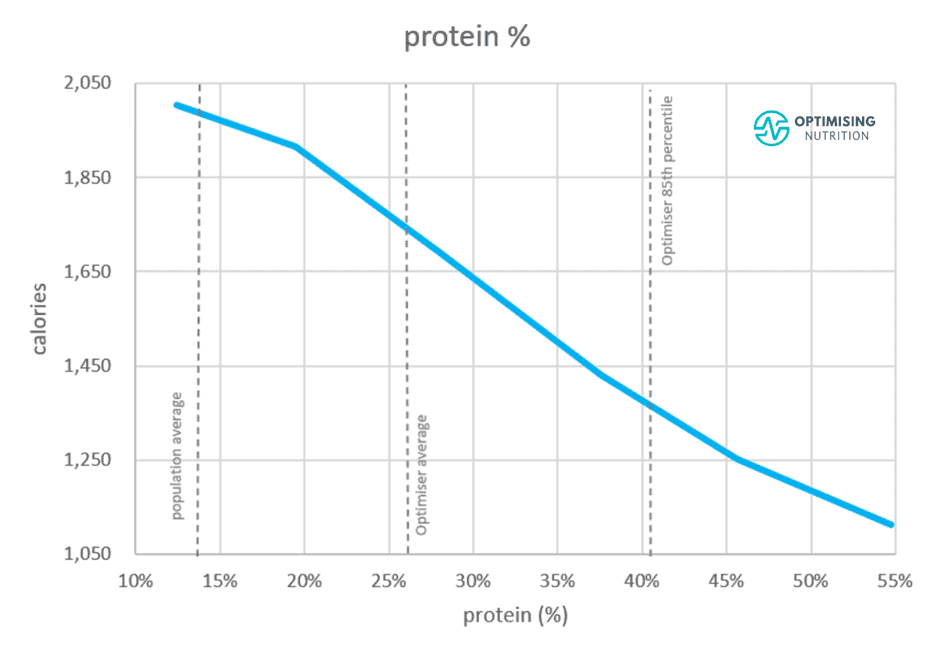
How Much Do Low Energy Dense Foods Impact Satiety?
But how much difference does moving from high to low-energy-density foods make?
The chart below shows the effects low and high-energy density foods have on satiety.
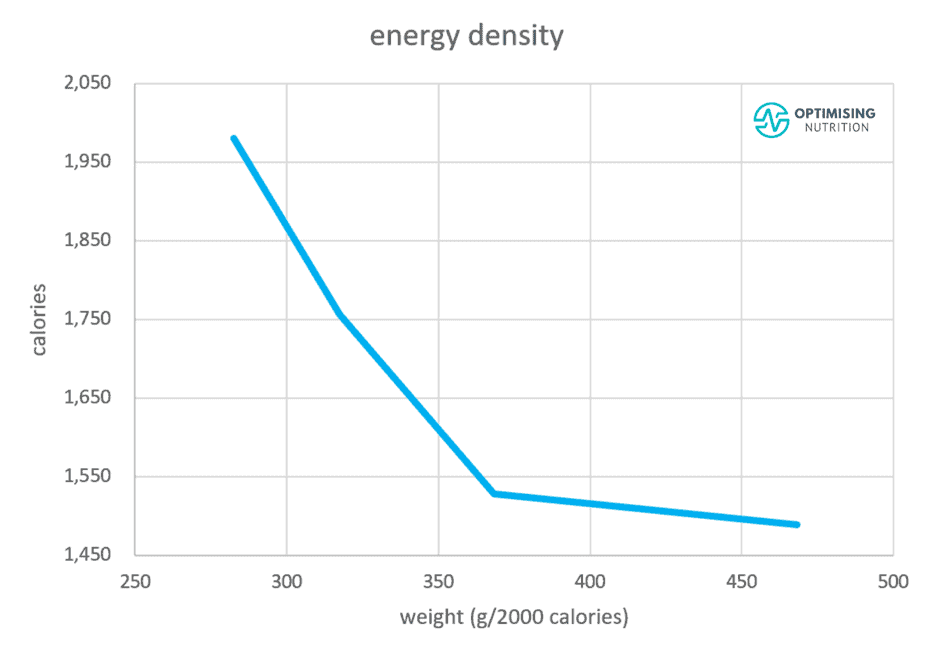
When we move from foods with less weight per calorie (more energy-dense) to more weight per calorie (less energy-dense), overall energy intake is reduced by 30%.
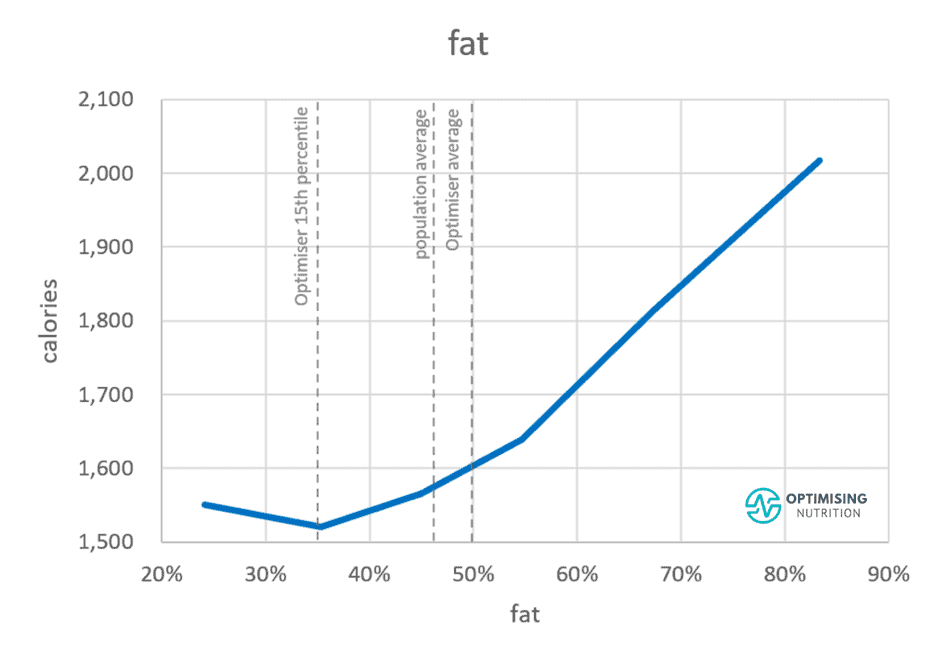
- Foods with a higher energy density to the left of this chart mainly consist of fat.
- Conversely, foods towards the right with a lower energy density consist mainly of carbohydrates, protein, fibre, and water.
It’s worth noting that we get most of the benefits when we move from very energy-dense foods to moderately energy-dense foods. Moving to extremely low energy-density foods doesn’t provide much additional benefit.
Our data analysis also shows that as you reduce your intake of (energy-dense) fat-containing foods, it becomes harder to overeat these (low energy-dense) low-fat foods.
But Is Low-Fat Really Where It’s At?
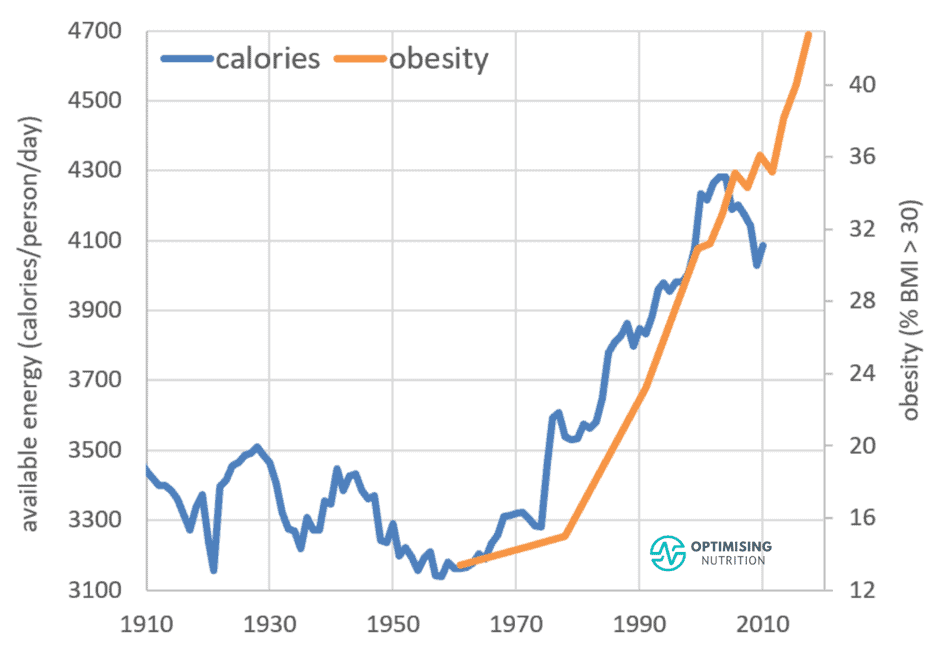
The idea of reducing our intake of high-fat foods has been the cornerstone of the ‘conventional nutritional wisdom’ for decades, particularly since the 1977 Dietary Guidelines for Americans was introduced.
We have been advised to minimise our consumption of fat because it contains more than twice as many calories per gram as carbs and protein. But sadly, in spite of trying to follow this lower-fat advice, we have just eaten more and gotten fatter.
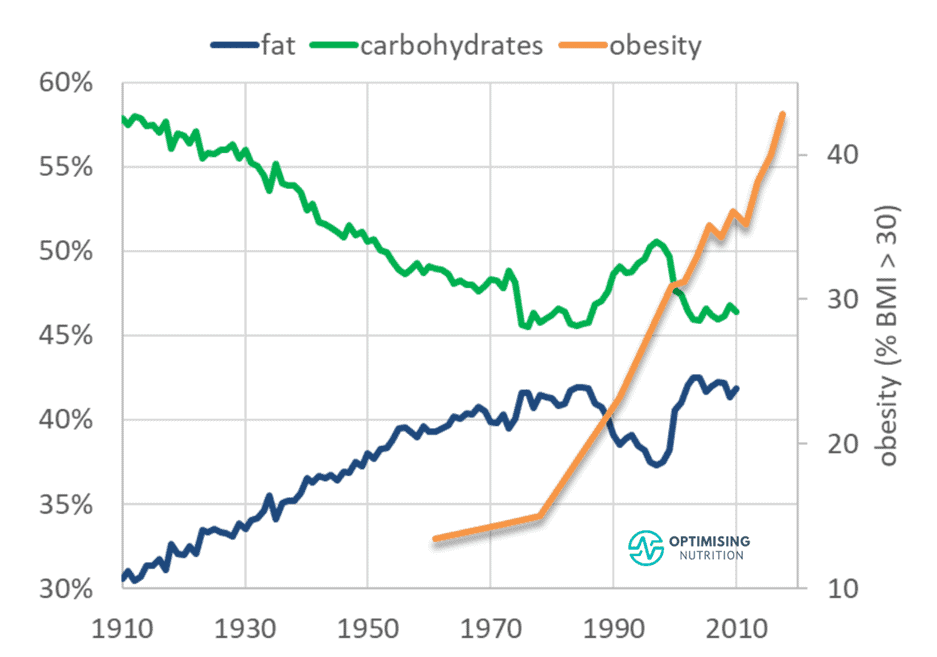
Over the past half-century, our intake of both fat and carbohydrates has increased.
Food processing has enabled more of our foods to become a similar mixture of fat and carbohydrates.
Do High-Volume Foods Make You Feel Fuller for Longer?
People who promote a vegan or plant-based lifestyle point out that high-fat foods are not as filling as fruits and vegetables.
Plant-based diet advocates like Joel Fuhrman and Neal Barnard talk about low energy density as a critical element of the effectiveness of their programs.

Professor Barbara Rolls has also published the Ultimate Volumetrics Diet based on her research into low-energy density foods. Professor Rolls’ diet plan is based on the idea that people typically eat a constant weight of food. While this is partially true, it’s not the whole story, particularly over the longer term.
Satiety vs Satiation
Before we dig deeper into the data analysis, it’s essential to understand the difference between satiety and satiation.
- Satiation occurs when we feel full after eating and no longer want to eat.
- Satiety is a longer-term phenomenon that occurs when we obtain enough of all the essential nutrients like the vitamins, minerals, amino acids, and fatty acids we require. Thus, we don’t search for more or as much food for a longer time.
Although low-energy-density foods might make you feel full in the short term, our analysis suggests that you might search for food again before too long. While low-energy-density foods provide some essential vitamins and minerals, they don’t supply the complete array of nutrients you need, particularly amino acids, selenium and zinc.
Consider how a big bowl of watery soup may leave you feeling full immediately after you eat it. However, there’s a good chance you’ll be hunting for some more energy-dense foods in only a few hours.
Conversely, low-energy-density veggies alongside a lean steak may keep you from thinking of food for many more hours. So, while this meal provides more calories, it’s likely to bring you satiation and satiety for long and short-term satisfaction that will allow you to eat less.
What Other Factors Align With Satiety?
While low-energy-density foods tend to align with a lower energy intake, our analysis shows that numerous quantifiable food parameters also affect whether (or not) we will eat less across the whole day.
The table below shows a selection of these parameters ranked by the most to least substantial effect each has on satiety based on our analysis of 125,761 days of data from 34,519 Optimisers.
- For example, we tend to consume 55% fewer calories each day when we move from a diet with a low percentage of total calories from protein (protein %) to a very high protein % diet.
- Energy density comes in at number 19 on this list of parameters that positively affect satiety.
| Rank | nutrient | satiety benefit |
| 1 | protein % | 55% |
| 2 | potassium (g/cal) | 49% |
| 3 | methionine (g/cal) | 43% |
| 4 | valine (g/cal) | 42% |
| 5 | diet quality | 41% |
| 6 | cystine (g/cal) | 41% |
| 7 | isoleucine (g/cal) | 40% |
| 8 | phenylalanine (g/cal) | 40% |
| 9 | lysine (g/cal) | 40% |
| 10 | histidine (g/cal) | 40% |
| 11 | threonine (g/cal) | 40% |
| 12 | tyrosine (g/cal) | 38% |
| 13 | phosphorus (g/cal) | 38% |
| 14 | tryptophan (g/cal) | 37% |
| 15 | cholesterol (%) | 33% |
| 16 | folate (g/cal) | 33% |
| 17 | calcium (g/cal) | 33% |
| 18 | niacin (B3) (g/cal) | 32% |
| 19 | energy density | 30% |
| 20 | vitamin B5 (g/cal) | 28% |
| 21 | riboflavin (B2) (g/cal) | 28% |
| 22 | iron (g/cal) | 28% |
| 23 | selenium (g/cal) | 26% |
| 24 | sodium (g/cal) | 24% |
| 25 | vitamin A (g/cal) | 23% |
| 26 | magnesium (g/cal) | 22% |
| 27 | fibre: carb ratio | 21% |
| 28 | vitamin B6 (g/cal) | 20% |
| 29 | vitamin K1 (g/cal) | 19% |
| 30 | leucine (g/cal) | 18% |
| 31 | thiamin B1 (g/cal) | 17% |
| 32 | vitamin E (g/cal) | 17% |
| 33 | fibre | 16% |
| 34 | manganese | 15% |
| 35 | vitamin C (g/cal) | 14% |
| 36 | zinc (g/cal) | 13% |
| 37 | omega 3 (g/cal) | 11% |
| 38 | vitamin B12 (g/cal) | 9% |
| 39 | copper (g/cal) | 8% |
To illustrate, while a lower energy density diet will help you eat 30% fewer calories across the day, moving from low to high protein % aligns with a 55% reduction in calories. That is, nearly twice the effect of a lower energy-density diet!
Does Adding Water to Your Meal Help?
The problem with energy density comes when we consider foods like fruit, watery soups, or shakes containing a significant amount of water.
While they may be filling in the short term because of their volume, they, unfortunately, don’t keep us satisfied for long, and definitely not satiated for the whole day.

As shown in the chart below, foods with a very low energy density do not provide greater satiety throughout the day. Once our food weighs more than about 500 g per 2000 calories, our energy intake throughout the day increases with these watery, low energy density foods.
Many people argue for drinking large amounts of water to ‘keep your stomach full’. While this has some merit–as thirst can be mistaken for hunger—water has very few (if any) nutrients. Thus, it does not satisfy your cravings for vitamins, minerals, essential fatty acids, or amino acids.
Many weight loss ‘gurus’ recommend drinking water with meals. However, this might do more harm than good for your digestion from a physiological perspective.
Your stomach contains concentrated amounts of hydrochloric acid (stomach acid) to break down your food. Similar to diluting acid in chemistry class, adding water when eating a meal tends to weaken your digestive ability. In theory, this could leave you absorbing fewer nutrients.
The bottom line is: liquid calories are not satiating over the long term. So if you want to feel fuller for longer, chew your food and don’t drink it!
Multivariate Analysis
The table above lists 39 factors that coincide with eating less across the day. However, all these food parameters don’t act independently.
Using multivariate analysis, we can tease out which factors affect satiety have the most statistically significant, independent effect on satiety.
Energy Density with Protein and Fibre
We know from our previous analysis that protein % and fibre are two key parameters that influence satiety over the longer term.
The table below shows the results of a multivariate analysis where we considered days of food with an energy density of fewer than 500 g/2000 calories (where we know energy density is actually helpful). The results of the multivariate analysis below show that:
- Protein % has a highly statistically significant impact on energy intake throughout the day. Moving from 22% to 44% protein reduces energy intake independently by around 33%.
- Fibre accounts for a significant but smaller 9% reduction in calories.
- Once we account for protein and fibre, a higher weight of food per calorie (lower energy density) corresponds with a 5% increase in energy intake across the day.
| Parameters | P-value | calories | % |
| protein (%) | 0 | -502 | -33% |
| fibre (%) | 2.4E-73 | -130 | -9% |
| weight (g/2000 cal) | 7.4E-21 | 84 | 5% |
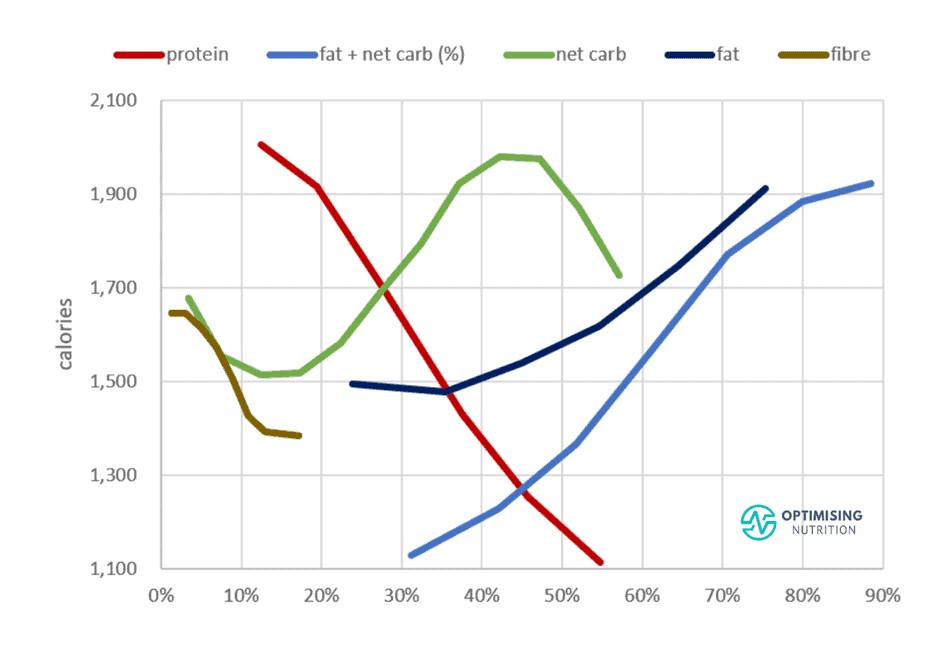
The chart below shows the interplay between macronutrients and average daily energy intake. It’s not just about reducing fat to increase satiety. Instead, it’s about reducing energy from both fat and carbs while prioritising foods with more fibre and–most importantly–a higher protein %.
Reducing either fat or carbs impacts daily energy intake similarly. However, limiting energy from carbs and fat while increasing protein % has the most significant effect on satiety and will keep you feeling satisfied for longer!
Energy Density with Protein, Fibre, and Micronutrients
Next, we’ll look at our multivariate analysis for energy density with protein, fibre, and various micronutrients included as well.
| P-value | calories | % | |
| protein (%) | 0 | -418 | -27.3% |
| potassium (mg/2000 cal) | 2.9E-59 | -137 | -9.0% |
| calcium (mg/2000 cal) | 1.7E-11 | -50 | -3.2% |
| fibre (%) | 1.6E-08 | -47 | -3.1% |
| sodium (mg/2000 cal) | 0.022 | -13 | -0.8% |
| weight (g/2000 cal) | 5.5E-22 | 86 | 5.6% |
The results of the multivariate analysis show that:
- Moving from low-protein to high-protein corresponds with a 27% reduction in calories.
- Moving from lower to higher intakes of potassium, calcium, fibre, and sodium per calorie also corresponds with a lower calorie intake.
- The multivariate analysis shows that some of the satiety benefit previously attributed to protein is actually due to other micronutrients.
- Once the other parameters are considered, a lower energy density has an overall disbenefit to satiety.
- Lower energy-dense foods correspond to a 6% increase in calories throughout the day.
The bottom line: Once you accurately account for other factors that have a statistically significant effect on satiety, the benefit of lower energy density disappears.
Once you have dialled in nutrient density, worrying about a lower energy density appears to be a bad idea!
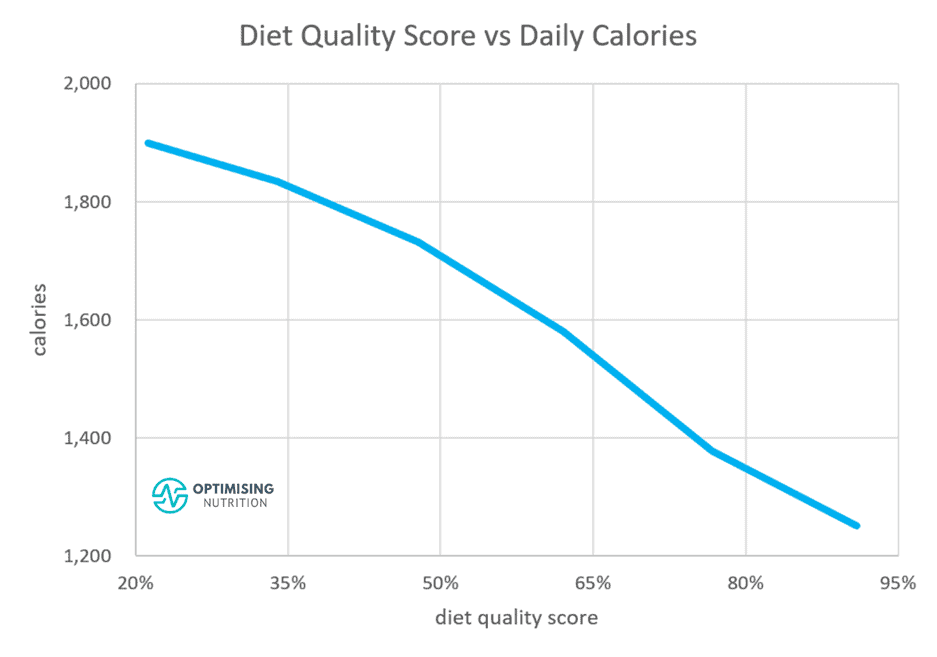
Diet Quality Is King!
If you want to improve your satiety across the day, it’s better to focus on foods and meals with a higher nutrient density to ensure you get the protein, vitamins, and minerals you require at the expense of minimal energy.
The chart below shows the micronutrient profile of the top 50 NutriBooster Recipes in terms of nutrient density, showing that we easily meet the Optimal Nutrient Intake stretch for all of the micronutrients.
By comparison, if we rank the recipes by energy density, we get a much lower overall nutrient density score. We end up missing out on several essential nutrients, including selenium, zinc, thiamine, niacin and all of the amino acids.
Short-term feelings of fullness from soups and shakes are not particularly helpful if your body craves the other essential nutrients it needs to thrive and goes in search of more food as soon as the bulky meal clears through your stomach.
The chart below illustrates how improving diet quality by optimising nutrient density will significantly enhance your satiety, reduce your cravings, and lower the quantity of food you tend to eat.
How Can I Reduce My Energy Intake?
If you want to increase your satiety and reduce how much you eat across the day, targeting nutrient-dense foods is more effective than low energy-density foods.
You can optimise your nutrient density by increasing your intake of foods that contain more nutrients with less energy. This is illustrated in the nutrient-dense foods chart below (download printable .pdf version here).
Simply focusing on low-energy foods might not supply you with an adequate amount of the essential micronutrients. As a result, only eating low-energy density foods can increase calorie intake because they are less satiating over the long term.
Nutrient-Dense Foods
Finally, the lists below illustrate what nutrient-dense foods look like. As you can see, they still have a fairly low energy density but a high nutrient density to ensure you get everything your body requires from the food you eat.
Plant-based foods
| names | nutrient density | energy (kcal/100g) |
| watercress | 86% | 15 |
| asparagus | 82% | 25 |
| chard | 80% | 24 |
| parsley | 80% | 44 |
| broccoli | 78% | 33 |
| chives | 77% | 37 |
| endive | 74% | 20 |
| lettuce | 70% | 21 |
| cauliflower | 69% | 30 |
| zucchini | 66% | 20 |
| alfalfa | 63% | 31 |
| green peas | 58% | 83 |
| green peppers | 57% | 24 |
| sauerkraut | 55% | 22 |
| cucumber | 54% | 18 |
| cabbage | 53% | 28 |
Animal-based foods
| names | nutrient density | energy (kcal/100g) |
| beef liver | 76% | 130 |
| chicken liver | 76% | 165 |
| lamb liver | 72% | 134 |
| ground pork | 60% | 185 |
| whole egg | 60% | 139 |
| duck eggs | 59% | 181 |
| pork ribs | 59% | 216 |
| milk | 57% | 42 |
| roast beef | 57% | 219 |
| egg white | 49% | 48 |
Seafood
| names | ONI score | energy (kcal/100g) |
| crab | 77% | 78 |
| crayfish | 76% | 78 |
| anchovy | 70% | 203 |
| oyster | 70% | 49 |
| cod | 69% | 273 |
| shrimp | 67% | 113 |
| squid | 67% | 87 |
| caviar | 65% | 276 |
| salmon | 64% | 156 |
| haddock | 63% | 85 |
| tilapia | 63% | 96 |
| herring | 63% | 210 |
| trout, cooked | 61% | 183 |
| halibut | 61% | 86 |
Nutrient-Dense Recipes
Some examples of our most nutrient-dense NutriBooster recipes are listed below:
- quick mackerel salad
- salmon tray bake
- salmon, chicory, sauerkraut & greens (pictured)
- turkey & spinach egg white omelette
- prawn, salmon, shiitake & cabbage stir fry
How Can I Calculate My Nutrient Intake?
If you’re interested in how ‘nutrient-dense’ your current diet is, you can see your nutrient profile for free using our 7-Day Nutrient Clarity Challenge.
After tracking your current diet in Cronometer for a week, our Nutrient Optimiser software will give you a prioritised list of foods and NutriBooster recipes to help you plug any nutritional gaps you may currently have.
Level Up Your Nutrient Density
To help you level up your nutrient density, we’ve prepared a Nutritional Optimisation Starter Pack to ensure you’re getting all the essential nutrients from your everyday foods.
This free starter pack includes:
- Maximum Nutrient Density Food List
- Sample Maximum Nutrient Density Recipe Book
- Sample Maximum Nutrient Density Meal Plan.
To get started today, all you have to do is join our new Optimising Nutrition Group here.
Once you join, you will find the Nutritional Optimisation Starter Pack in the discovery section here.









(applause)–now write the same type of article with the same type of info LOOKING THROUGH THE LENS OF HISTAMINE INTOLERANCE, because that’s where I am right now. Making the transfer from winter eating to spring eating has set off a huge (for me) histamine response. I’m having to get by on a very small subset of foods and lots of supplements to cope. Hopefully this will pass soon, as I’d really like to get back to eating with the seasons and lose my winter weight. Histamine intolerance calls for a blend of some keto foods, some higher-carb foods (which I try to avoid), and grass-fed meats.
The Low Histamine Diet isn’t meant to be permanent because it’s so restrictive, so I’m going to have to figure out my list of nutrient-dense, yet low-histamine foods (that’s where I’d like your help).
I may find that making the switch from keto to PSMF just isn’t good for my body, and may have to resort to leaving out a season, or extending a season, for this experiment in order to make it through an entire year.
Lookie what I found this morning: https://consumer.healthday.com/aha-news-want-a-personalized-diet-to-prevent-disease-nutrition-scientists-are-working-on-it-2656969203.html
It seems the U.S. National Institute of Health is finally coming around to the fact that personalized diets are needed, and plan to use an algorithm to do it–I wonder…are they going to rip off YOUR expert-built system, or are they going to reinvent the wheel? Knowing that these are bureaucrats, they’re likely to build/obtain a bare bones version of what you have here. I hope you adequately protected your system and data.