Step into the realm of nutritional ketosis and untangle the myths surrounding ketone levels.
This in-depth article illuminates the ideal ketosis level for shedding pounds and the reality behind the much-debated concept of ‘optimal nutritional ketosis’ to help you understand the nuances of nutritional ketosis. As with most things in life, more may not be better.
Delving into real-world experience, scientific evidence, and real-world data, this article aims to challenge and bring clarity to some of the popular keto narratives.
It also seeks to equip you with the insights needed to leverage ketosis for enhanced metabolic health.
Embark on an eye-opening journey that could redefine your approach to the ketogenic lifestyle and help you reach your weight loss goals more effectively.
‘Optimal Nutritional Ketosis’
In 2013, I watched Jimmy Moore lose a massive amount of weight while tracking his ketones. It appeared that nutritional ketosis equated to fat loss. I wanted in!
So, I grabbed a blood ketone meter and started testing to see if I could get high ketones. Unfortunately, this made me fatter and more inflamed. The photo below is my work profile photo during my ‘keto harder’ phase at that time.
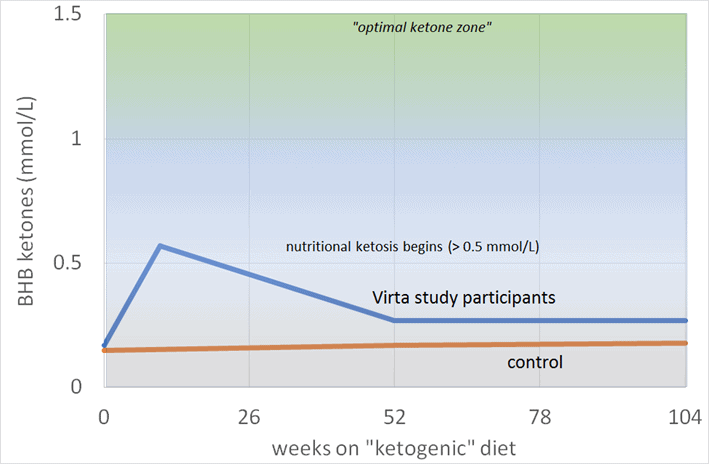
Much of the confusion around ‘optimal ketosis’ seems to be rooted in the ‘optimal ketone zone’ chart shown below, initially published in Phinney and Volek’s Art and Science of Low-Carbohydrate Living.
According to this chart, a ‘ketogenic diet’ generates blood ketone values greater than 0.5 mmol/L., also known as ‘nutritional ketosis’. But, if you want ‘optimal nutritional ketosis’, you need to get your ketones above 1.5 mmol/L.
Some keto gurus have suggested that you should do whatever it takes to get your ketones into the ‘optimal ketone zone’ by any means possible. With ketones as the end goal, many recommend increasing butter, MCT oil, and exogenous ketone supplements if you want to lose weight and improve your health.
Many people advocating for this were part of a popular multi-level marketing scheme for exogenous ketone supplements. This may have clouded their judgement and recommendations.
I had the privilege of having Professor Steve Phinney (pictured below in our kitchen) stay at our place for a couple of days when he spoke at a Low-Carb Down Under event in Brisbane in 2016. During that time, I took the opportunity to quiz him about the basis of the ‘optimal ketosis’ chart.
Steve told me the chart was based on the blood ketone levels of participants in two studies done in the 1980s. The first was with cyclists who had adapted to ketosis over six weeks. The second was a weight loss study where people were put on a ketogenic diet. In both cases, the critical thing to note is that ‘optimal ketone levels’ between 1.5 and 3.0 mmol/L were observed in people who had recently transitioned to a lower-carb diet.
However, as more people have ‘gone keto’, many people find their blood ketone levels continue to decrease after a few weeks or months on a ‘ketogenic diet’.
Even Keto Clarity author Jimmy Moore has stated that elevated ketones will not lead to weight loss, and there is no use in tracking them!
We now know that ketone levels in our blood decrease as we become more metabolically healthy and better at burning ketones for fuel rather than having them back up in the bloodstream. In addition, it is now apparent that most people move beyond the ‘keto-adaptation phase’ after a few weeks or months as their bodies learn to use fat more efficiently.
Interestingly, the Inuit have a genetic adaptation that causes them to see lower levels of ketones on a high-fat diet. This is interesting because they are often used as an example of people who thrive on a very low-carb diet.
This progressive adaptation on their quest for nutritional ketosis leaves many people faced with the decision to either:
- continue to add more refined fat from calorie-dense butter, MCT oil, and exogenous ketones to maintain elevated ketones in pursuit of ‘optimal ketosis’, or;
- reduce dietary fat to use body fat for energy, thus improving their metabolic health, reversing their diabetes, and reducing or obliterating obesity.
In an attempt to understand what was really happening, I compiled some data from my own testing and from friends and family who were also tracking their blood sugar and ketone values.
I wanted to understand what typical ketone levels were for people who reported that they had been following a reduced carbohydrate diet for more than a few weeks. Later, Michel Lundell from Ketonix shared an extensive set of anonymised data.
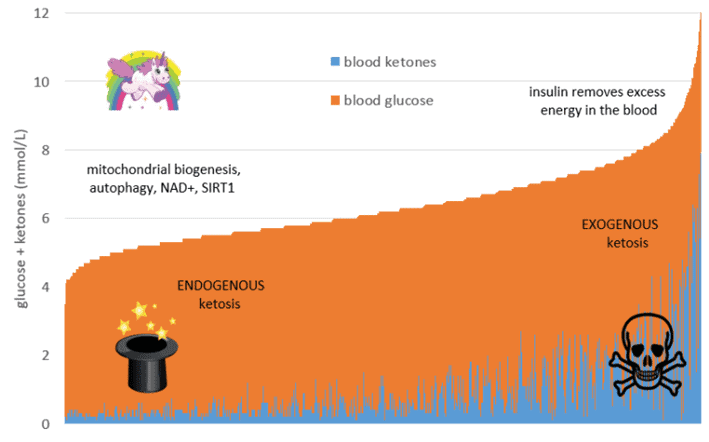
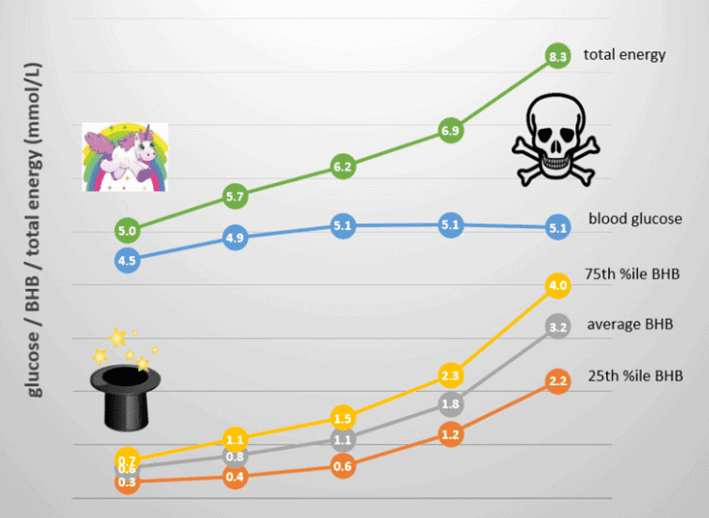
The chart below shows the sum of the blood sugar and ketones (i.e. total energy) from a broad range of people following a low-carb or ketogenic diet, represented as nearly 3000 data points. Blood ketones are shown in blue (on the bottom), while glucose is shown in orange (on the top).
On the right-hand side of the chart, we have a high-energy state where both glucose and ketones are elevated simultaneously. While some people have high ketones and low blood glucose from endogenous ketosis, some people have high glucose and high ketones together. However, this is likely exogenous ketosis that has resulted from consuming high levels of dietary fat or ketone supplements.
This high-energy situation is similar to someone with untreated Type-1 Diabetes, where high glucose and high ketone levels result from inadequate insulin production. Uncontrolled by adequate insulin, their stored energy flows into their bloodstream, and they see elevated levels of glucose, ketones, and free fatty acids.
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a very dangerous state that usually only occurs in someone with uncontrolled Type 1 Diabetes. It is diagnosed when someone has glucose levels above 13.9 mmol/L or 250 mg/dL and significant ketones. This would equate to a quantity of total energy in the bloodstream of 11.5 mmol/L from glucose and ketones.
People with a healthy and functioning pancreas don’t tend to see these extremely elevated levels. However, some people with glucose and ketone levels to the right of this chart are definitely on the spectrum of extreme energy toxicity.
While DKA and ‘nutritional ketosis’ are different, we must stop and wonder whether having excessive amounts of energy in our bloodstream (i.e. energy toxicity) is desirable.
On the left-hand side of the chart, we see people with lower total energy in their bloodstream. We often refer to people who have plenty of storage available for glucose or fat as ‘metabolically flexible‘.
Because they store and use fuel efficiently, metabolically healthy people don’t need large amounts of energy circulating in their bloodstream. Their fat stores are not overfilled, and they can easily hold fuel in storage and not in their bloodstream. As a result, their liver releases just enough energy into their blood when they need it to support their activity.
Some people come to keto to manage chronic conditions such as cancer, epilepsy, traumatic brain injury or dementia. These people appear to benefit from high blood ketones fuelling the brain when glucose cannot be used efficiently.
If you are trying to avoid muscle wastage from cancer cachexia or if you’re trying to feed a growing child with epilepsy, an energy-dense, high-fat, low-satiety diet can help them gain weight while maintaining high levels of ketones.
People following a therapeutic ketogenic diet often load up with MCT oil and other added fats to achieve high ketone levels. Others target high levels of ketones with hopes of increased mental performance by loading up on exogenous ketones and glucose together to ‘dual fuel’ for elite athletic performance.
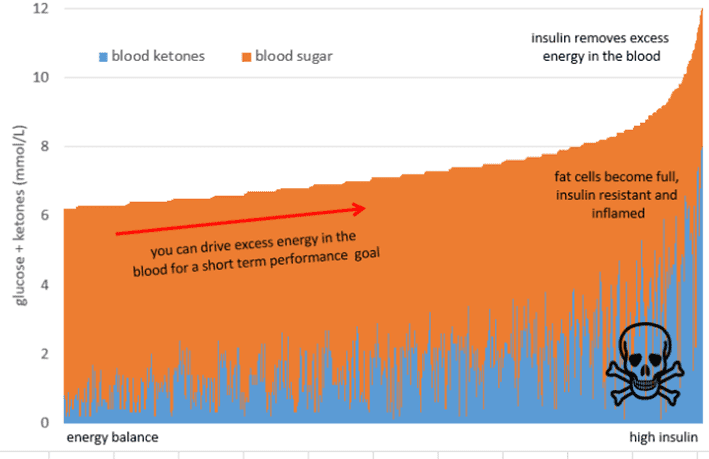
Although having sky-high levels of energy in your bloodstream may be beneficial if you’re about to race in the Tour de France, chronically high energy from glucose and ketones simultaneously is not ideal if you are sedentary, trying to lose weight, or want to reverse your Type-2 Diabetes.
Most people do not require ‘therapeutic ketosis’, especially if weight loss or blood sugar control are their primary goals. These people need to optimise their diet to move towards a lower energy state to allow the stored energy on their body to be used.
The danger with trying to drive high levels of ketones by eating more fat is that it will lead to energy toxicity. This will drive up insulin and promote even more fat storage over the long term.
To summarise, for healthy weight maintenance, you want to see a total energy (from both glucose and BHB together) in your bloodstream less than 6 mmol/L. However, if you’re losing weight, you may see this drift down towards 4.0 mmol/L.
How to Reverse Energy Toxicity
On the left-hand side of the total energy chart (i.e. glucose and ketones together), we have endogenous ketosis or ketones produced from utilising body fat for energy. By decreasing energy levels from glucose and fat in your blood, your body draws on your fat stores to compensate for the energy deficit. It will also use excess stored fat and old proteins in your liver, pancreas, brain, and other organs in a process known as autophagy.
This is a great place to be if you are trying to reduce your blood sugar, lose body fat, or improve your general metabolic health. As indicated by the little unicorn on the left of the charts, the real magic of ketosis happens when the ketones come from the fat on your body (endogenous ketosis) and not from energy sources like fat from outside your body (exogenous ketosis).
Reducing carbohydrates is beneficial if it moves you away from hyper-palatable processed foods that contain a hearty combination of carbs and fat. However, excessive levels of dietary fat will not be optimal if they lead you to increase your overall energy intake significantly.
Hopefully, you can see that pursuing ‘optimal’ ketone levels as the primary end goal can be dangerous. If eating a ‘ketogenic’ diet causes you to add more nutrient-poor, low-satiety refined fat to your diet, it can worsen your insulin resistance and increase your body fat.
Dietary fat doesn’t abruptly raise your insulin levels over the short term. However, as we’ll see later in Keto Lie #5, it can still easily contribute to your body fat. In this sense, it can increase your insulin levels and insulin resistance.
The increased energy levels in your blood (in the form of glucose, ketones and free fatty acids) will quickly lead to increased energy stored as fat in your body and increased insulin to hold that fat in storage.
What Happens to Ketones on a ‘Ketogenic Diet’ Over the Long Term?
It’s interesting to see how the crowd-sourced ketone data in the charts above aligns with the Virta study’s one-year results (Phinney et al., 2017). This study aimed to get 262 participants with Type-2 Diabetes into nutritional ketosis to improve blood sugar management and reverse diabetes.
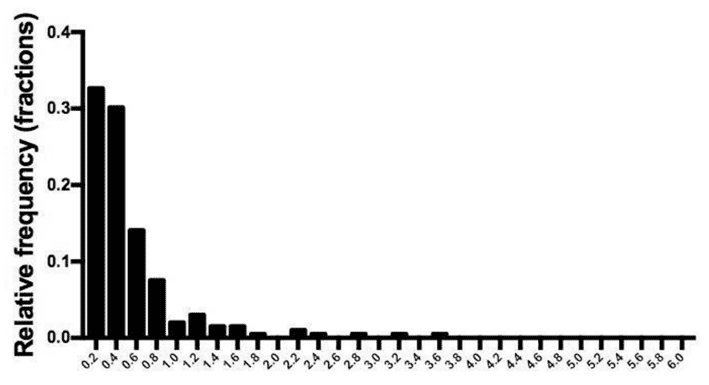
The distribution of BHB levels after ten weeks of the Virta trial is shown in the chart below. While several people had higher ketone values, many people had values of less than 0.5 mmol/L, even during the initial adaptation phase.
Despite consuming a ‘ketogenic diet’ under the supervision of the Virta Team, led by Steve Phinney, most study participants did not achieve ketone levels that qualified as ‘nutritional ketosis’ (BHB > 0.5 mmol/L) according to the ‘optimal ketone zone’ chart.
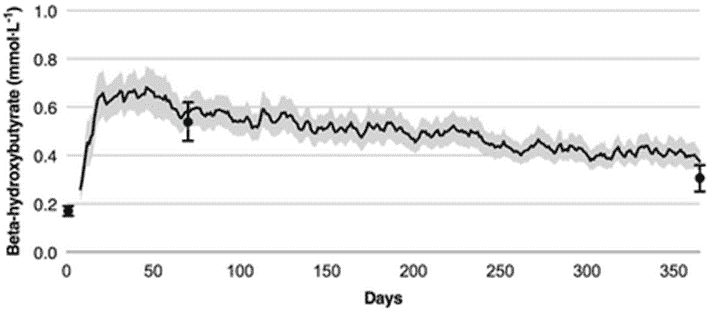
The following chart shows the average ketone levels of people participating in the Virta study over the first year (from Effectiveness and Safety of a Novel Care Model for the Management of Type 2 Diabetes at 1 Year: An Open-Label, Non-Randomized, Controlled Study).
We see that blood ketone levels initially rose from 0.18 mmol/L at baseline to 0.6 mmol/L in the first few weeks. However, after a year, blood ketone values decreased to 0.27 mmol/L. This is well below the minimum threshold for nutritional ketosis of BHB > 0.5 mmol/L and far from the ‘optimal ketone zone’ of BHB > 1.5 mmol/L.
As shown in the chart below, blood ketone levels remained at 0.27 mmol/L after two years of Virta participants following a ‘ketogenic diet’ as people continued to lose weight and improve their diabetes (data from Long-Term Effects of a Novel Continuous Remote Care Intervention Including Nutritional Ketosis for the Management of Type 2 Diabetes: A 2-Year Non-randomised Clinical Trial).
This data on the ketone levels of people adhering to a long-term keto diet was buried in the back of the paper and not discussed at all. If I had my way, the headline of the paper would have been, ‘Blood ketone values are negligible after two years on a ‘well-formulated ketogenic diet’ as participants lost weight, reversed their diabetes and improved their metabolic health. So, why the hell are we still telling people to test ketones?’
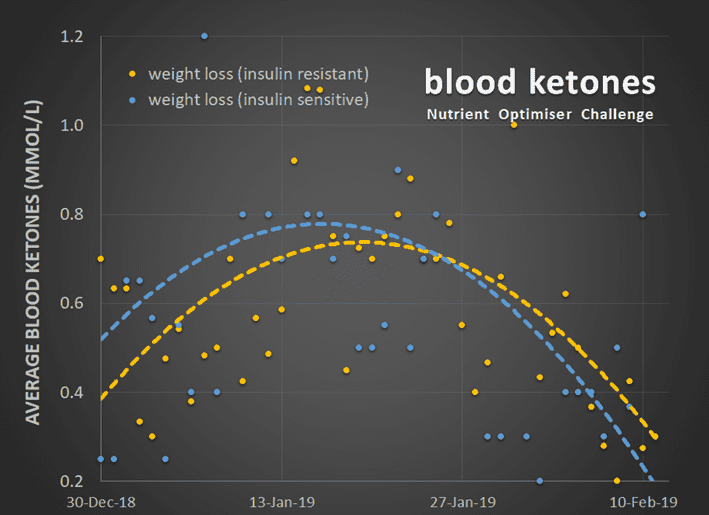
As shown in the chart below, we have seen a similar trend with ketones in our Nutritional Optimisation Masterclass. Blood ketones tend to rise for a couple of weeks when people focus on nutrient-dense, high-satiety foods and meals and start to lose weight. But after a few weeks, blood ketone levels decreased as people continued to lose weight and lower their blood sugars.
As you can see from the blue and orange trend lines, people who self-identified as insulin-resistant saw their blood ketones rise more slowly. However, they stayed elevated for longer as weight loss continued.
People who are physically fit and with better markers of metabolic health (i.e. lower blood sugars, lower body fat, more lean mass and lower waist-to-height ratio) tend to have lower blood ketone levels. They also tend to have lower blood sugar levels, especially after following a low-carb or ketogenic diet for several weeks. Once your liver, muscles, and body fat are not filled to the brim with energy, it no longer overflows into the bloodstream.
Once your body uses your excess energy, such as the glucose and ketones in your blood, it gets on with using the fat on your body. Once you start to deplete the excess energy in your body, you are unlikely to see high energy levels backing up and overflowing into your blood.
What Are Optimal Ketone Levels for Fat Loss and Nutritional Ketosis?
When it comes to defining ‘optimal ketone levels’, we need to be mindful of several things.
- While ketone levels can be elevated for a few weeks on a ‘ketogenic diet’, our bodies appear to adapt to using ketones more efficiently and (or) revert to using the citric acid cycle rather than ketosis to oxidise fat.
- Elevated ketone levels are associated with a high-energy state, fuelled by increased dietary fat or exogenous ketones. This may be beneficial for elite athletic performance or the management of epilepsy, Alzheimer’s, and dementia.
- But if your goal is fat loss and improved metabolic health, we want a lower overall energy state where we generate ketones from body fat.
To clarify the topic of ‘optimal ketosis’, I prepared a chart that shows the range of blood ketones, blood sugar, and total energy you might expect to see when following a low-carb or ketogenic diet. The data is divided into five groups and is represented from the lowest to the highest total energy.
On the left, we have endogenous ketosis, where ketones are made from your body. On the right, we have exogenous ketosis, where ketones come from added dietary fat.
If you are part of the majority of people who want fat loss or improved metabolic health, you will want to move towards the left-hand side of this chart.
If you are on a ketogenic diet, relatively metabolically healthy and lean, and not overdoing the refined dietary fats, you will likely see BHB ketone values between 0.3 and 1.5 mmol/L.
Ketones will be higher if you fast, restrict calories, exercise, or consume more dietary fat. The level of ketones in your blood may be temporarily elevated when you start losing weight. However, it’s important to remember that this is a side effect of weight loss and not the cause.
If your goal is exogenous ketosis, where ketones are produced primarily from the fat in your diet for the management of epilepsy, Parkinson’s, or dementia, the ‘optimal ketosis’ values will be on the higher end of this range.
Remember that blood ketones will likely decrease over time as your metabolic health improves. As a result, many people conclude that blood ketones are not worth the expense, pain, or hassle.
Summary
- Your body produces ketones from your fat stores as an alternative fuel source for your brain and organs when there is no glucose, like when you go without food. This is known as endogenous ketosis because you are self-producing ketones in your liver from the fat on your body.
- When the supply of glucose and protein in our diet is reduced, our body can make ketones from the fat we eat. This is known as exogenous ketosis, or when the fuel for ketones is coming from outside the body.
- Most of the beneficial things we associate with ketosis, like autophagy, lowered blood sugars, diabetes reversal, and fat loss, occur when we use our body’s energy stores because we are eating less. We can’t ‘bio hack’ all these benefits by artificially elevating our blood ketone.
- We initially see higher beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) levels when people preliminarily switch to a low-carb or ‘ketogenic diet’.
- Ketones tend to peak once we have drained excess glucose from the blood and glycogen stored liver.
- Ketone levels tend to decline afterwards as people continue to lose body fat and improve their metabolic health as they reduce the amount of stored energy.
- Any diet that stimulates fat loss is likely considered ‘ketogenic’ because you will be burning stored body fat. However, measurable blood ketones will likely decrease as we lose fat and improve our metabolic health over time.
- It’s hard to make much sense of the number you see on your blood ketone meter to understand whether:
- you are in the early stages of fat loss and starting to release stored energy into your bloodstream or
- you are overloading your system with excess energy that you are using inefficiently.
- Most people do not achieve the minimum ketone level to qualify for ‘nutritional ketosis’ (BHB > 0.5 mmol/L), let alone ‘optimal ketosis’ (i.e. BHB > 1.5 mmol/L) without adding excessive amounts of dietary fat.
- Merely adding more dietary fat will slow body fat loss, increase insulin levels throughout the day, and worsen metabolic health.
- While reducing dietary carbohydrates may help to stabilise blood sugars and improve satiety, tracking BHB is of limited use to help you optimise your diet or make more intelligent nutritional choices.
The Reality for Nutritional Ketosis
So, it seems that ‘keto’ has an identity problem.
- The most widely accepted definition of nutritional ketosis is one that increases BHB above 0.5 mmol/L.
- However, we only see BHB ketones greater than 0.5 mmol/L in people who:
- have recently transitioned to a low-carb or ketogenic diet,
- are fasting for an extended period or
- are adding copious amounts of refined dietary fat or exogenous ketones to their diet.
- To maintain elevated ketone (BHB) levels, you must continue to increase the amount of nutrient-poor, low-satiety dietary fat, which can quickly lead to weight gain.
There are innumerable benefits from a diet that contains less processed carbohydrates. However, ‘keto’ has an identity problem by definition that is sadly causing many people to worsen their metabolic health, insulin resistance, obesity, and diabetes.
I would dearly love to see the ‘optimal ketone chart’ retracted. I believe it is potentially dangerous advice and has led many people, including myself, to worse metabolic health.
I published a blog post on this topic in July 2015 that has received nearly 383,638 views. I’ve also left plenty of comments on the Virta Facebook Page, where I shared my insights. Sadly, most of them were deleted.
I have spoken to Professor Steve Phinney, author and podcaster Jimmy Moore and several other ‘keto gurus’ about this. Sadly, a large industry has built up around the strict ‘keto’ belief that elevated ketones are an end goal and the secret to optimal health.
Get your copy of Big Fat Keto Lies
I hope you’ve enjoyed this excerpt from Big Fat Keto Lies. You can get your copy of the full book here.
What the experts are saying about Big Fat Keto Lies
More
- Big Fat Keto Lies: Now On Kindle
- Big Fat Keto Lies: Introduction
- A Brief History of the Low Carb and Keto Movement.
- Keto Lie #2: You Have to be ‘in Ketosis’ to Burn Fat.
- Keto Lie #3: You Should Eat More Fat to Burn More Body Fat.
- Keto Lie #4: Protein Should Be Avoided Due to Gluconeogenesis.
- Keto Lie #5: Fat is a ‘Free Food’ Because it Doesn’t Elicit an Insulin Response.
- Keto Lie #6: Food quality is Not Important. It’s All About Reducing Insulin and Avoiding Carbs.
- Keto Lie #7: Fasting for Longer is Better.
- Keto Lie #8: Insulin Toxicity is Enemy #1.
- Keto Lie #9: Calories Don’t Count.
- Keto Lie #10: Stable Blood Sugars Will Lead to Fat Loss.
- Keto Lie #11: You Should ‘Eat Fat to Satiety’ to Lose Body Fat.
- Keto Lie #12: If in Doubt, Keep Calm and Keto On.
- Resources













…and to think that all it took to turn the MLM world into a pile of sand is a wee thing called a pandemic…