Vitamins, those tiny yet mighty compounds, play a vital role in keeping our bodies functioning at their best. But how do we ensure we’re getting enough of these essential nutrients? Welcome to our comprehensive guide on high-vitamin foods, where we unveil the secrets to boosting your vitamin intake effortlessly and deliciously.
Whether you’re battling fatigue, seeking stronger bones, or striving for a more robust immune system, our guide will lead you to a treasure trove of vitamin-rich foods that are nutritious and satisfying.
Get ready to transform your meals into power-packed, health-boosting delights that cater to your body’s needs and your taste buds’ cravings!
- Top 12 High-Vitamin Foods List
- What Are High Vitamin Foods?
- How Can I Get More Vitamins in My Diet?
- What Are the Benefits of High Vitamin Foods?
- Risks Associated with Excess Vitamin Intake
- How Much of Each Vitamin Do I Need?
- Vitamin-Rich vs High Vitamin Foods
- High-Vitamin Recipes
- High-Vitamin Meal Plan
- How Can I Know if I’m Getting Enough Vitamins?
- Appendix – High Vitamin Foods
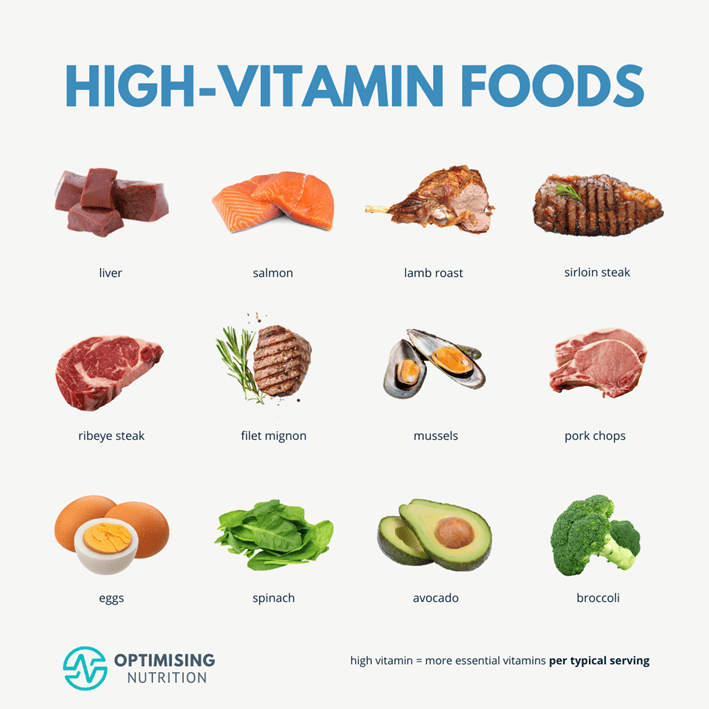
Top 12 High-Vitamin Foods List
Twelve of the top high-vitamin foods that pack in more vitamins per serving, popular with our Optimisers, are:
- liver
- salmon
- lamb roast
- sirloin steak
- ribeye steak
- filet mignon
- mussels
- pork chops
- whole egg
- spinach
- avocado
- broccoli
What Are High Vitamin Foods?
High-vitamin foods, detailed in our high vitamin foods list, contain more of all the essential vitamins per serving. Thus, they give you more of the essential vitamins per bite and enable you to boost your vitamin intake.
While vitamin-rich foods pack more vitamins with less energy, high-vitamin foods also contain the protein and energy you require daily.
How Can I Get More Vitamins in My Diet?
The best way to get your vitamins is through a balanced diet with a wide variety of nutrient-dense foods that also contain the vitamins and protein your body needs to thrive. This ensures you get all the essential nutrients to optimise your health and vitality.
When you’re ready to level up your vitamin game, check out the links below for longer PDF lists for each vitamin in our Optimising Nutrition Community:
- thiamine (B1)
- riboflavin (B2)
- niacin (B3)
- vitamin B5
- vitamin B6
- vitamin B12
- folate
- vitamin A
- vitamin C
- vitamin E
- vitamin K1
We’ve also included infographics at the end of this article showing foods that contain more of each vitamin per serving.
What Are the Benefits of High Vitamin Foods?
Vitamins are essential micronutrients that are crucial in maintaining overall health and well-being. Consuming a diet with plenty of vitamins can offer numerous health benefits, including:
- Enhanced Immune System: Vitamins A, C, and E act as potent antioxidants that help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. These antioxidants boost the immune system’s ability to combat infections and illnesses.
- Stronger Bones and Teeth: Vitamin D promotes calcium absorption, which is essential for maintaining bone density and preventing osteoporosis. Vitamin K1 also plays a role in bone health and helps prevent blood clots.
- Improved Cardiovascular Health: Vitamin C helps lower LDL cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease. Vitamin E protects blood vessels from damage and may help prevent stroke.
- Healthy Skin and Hair: Vitamin C is required for the production of collagen, a protein that gives skin structure and elasticity. Vitamin A promotes healthy cell growth and turnover, contributing to radiant skin and healthy hair.
- Enhanced Energy Levels: B vitamins, such as B1, B2, and B3, are involved in energy metabolism and help convert food into energy. Consuming adequate B vitamins can combat fatigue and boost energy levels.
- Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases: A diet rich in vitamins can help protect against various chronic diseases, including cancer, type 2 diabetes, and Alzheimer’s disease. Vitamins play a role in cellular processes that may reduce the risk of these conditions.
- Improved Cognitive Function: B vitamins, such as B6 and B12, are essential for brain function and may help improve memory, concentration, and overall cognitive performance.
- Healthy Vision: Vitamin A is crucial for maintaining healthy vision and preventing night blindness. Vitamin E may also protect against age-related macular degeneration.
- Stronger Muscles and Nerves: Vitamin B1 supports muscle function and nerve transmission. Vitamin B12 is essential for nerve cell growth and maintenance.
- Enhanced Mental Well-being: B vitamins, such as B5 and B9, play a role in regulating mood and reducing stress. Consuming adequate B vitamins may help improve mental well-being and reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Risks Associated with Excess Vitamin Intake
While vitamins are essential for our health, consuming excessive vitamin supplements can lead to serious health problems. This is known as vitamin toxicity or hypervitaminosis.
Fat-soluble vitamins, such as A, D, E, and K, are more likely to cause toxicity than water-soluble vitamins, as the body stores excess fat-soluble vitamins in the liver and fatty tissues. Meanwhile, water-soluble vitamins, such as vitamin C and B vitamins, are excreted in the urine, making it less likely to accumulate to toxic levels.
In our Micros Masterclass, we guide Optimisers to chase their priority micronutrients with whole foods. Continually focusing on the nutrients you’re getting less tends to ensure that people aren’t consuming a broad range of foods and avoiding excessive amounts of any single nutrient.
How Much of Each Vitamin Do I Need?
Our satiety analysis has provided unique insights into the minimum amount of each vitamin we crave.
- The ‘bliss point’ intake for each vitamin, shown in the table below, aligns with the maximum energy intake. If we get less than this amount, we’ll crave more food until we get the necessary vitamins.
- The Optimal Nutrient Intake (ONI) is our stretch target for each of the vitamins achievable with food but aligns with greater satiety because we satisfy our requirements for the vitamins with less energy.
| vitamin | Bliss Point (per 2000 cal) | ONI (per 2000 cal) | units |
| thiamine (B1) | 1.3 | 3 | mg |
| riboflavin (B2) | 1.4 | 4 | mg |
| niacin (B3) | 18 | 50 | mg |
| vitamin B5 | 3.9 | 10 | mg |
| vitamin B6 | 1.5 | 4 | mg |
| vitamin B12 | 3.6 | 8 | mcg |
| choline | 450 | 1000 | mg |
| folate | 380 | 1000 | mcg |
| vitamin A | 400 | 1200 | mcg |
| vitamin C | 55 | 160 | mg |
| vitamin E | 7 | 20 | mg |
| vitamin K1 | 55 | 140 | mcg |
Note: These values are shown per 2000 calories, so you will need to factor these up or down based on your current energy intake.
Our satiety analysis shows that foods that contain more vitamins per calorie tend to be more satiating. However, protein and minerals that are not used in fortification and supplements dominate the satiety equation, so don’t trust your multivitamin as ‘nutritional insurance’ to compensate for a low-satiety processed diet.
For more details, see The Role of Vitamins in Satiety and Weight Management.
Vitamin-Rich vs High Vitamin Foods
Foods high in vitamins will help you boost your vitamin intake if you are not yet meeting the minimum (bliss point) intake. Once you get the minimum amount of each vitamin, you can focus on vitamin-rich foods that provide more vitamins with fewer calories.
In our Micros Masterclass, we guide our Optimisers to use high-vitamin foods to meet the minimum vitamin requirements. From there, they can use vitamin-rich foods to get more vitamins with less energy and move towards the Optimal Nutrient Intakes to boost satiety, nutrient density and vitality.
High-Vitamin Recipes
If you’re looking for high-vitamin recipes, check out our NutriBooster recipes, designed to maximise nutrient density while aligning with different goals and preferences.
High-Vitamin Meal Plan
To see what a week of eating foods high in vitamins looks like, download our free Healthiest Meal Plan in the World here.
How Can I Know if I’m Getting Enough Vitamins?
The best way to know if you’re getting the required vitamins is by tracking your food intake for a few days in Cronometer.
Take our Free Nutrient Clarity Challenge. You’ll discover which vitamins you’re missing and the foods and meals that contain all your priority nutrients.
If you’re ready to take your nutrition to the next level, we’d love you to join our Micros Masterclass.
More
- High Mineral Foods
- Mineral Rich Foods
- Vitamin Rich Foods
- The Role of Vitamins in Satiety and Weight Management
- Level Up Your Health with Gamified Personalised Nutrition
- Micros Masterclass
Appendix – High Vitamin Foods
The infographics below show popular foods that provide more of each of the essential vitamins per serving. Below each food, the amount of each vitamin provided by the typical serving size consumed by our Optimisers is also shown.